Master the Pawn Structures in Chess and Crush Your Opponents!
⭐⭐⭐ Take 4 minutes to read and improve your chess game ➡️ : This article was first published on, and is Copyright of Chessquestions.com
In any game of chess, the pawn structure is always important to consider. Pawns can tell you a lot about your opponent’s strategy, and it is essential to be aware of this in order to make good decisions yourself. In particular, knowing when your pawns are weak and need to be protected is critical for success. So if you’re looking to improve your game, it is essential to learn how to recognize pawn structures and exploit them to your advantage!
What is Pawn Structure in Chess
Pawn structure is the positions of all pawns, black and white, at a relevant point during a game on the chessboard dictating to intermediate and advanced players what point of the strategy has been reached and determining which are the best move options to come for either side.
As chess ability increases, it becomes more important to understand pawn structure as part of the game and to be able to recognize the structure at any given time. This understanding not only provides huge clues as to what your best next move is, but also what your opponent should be thinking too, to provide you an insight into their thought process and the next step of their strategy.
Why You Need To Learn Chess Pawn Structures
The pawn structure at any given time determines what you should be doing next, or indeed more interestingly, what your position needs to either make it stronger or if the structure now allows you to begin your middle game attack tactics.
Understanding what the pawn structure is and its strength will also let you know what position of advantage or disadvantage you are at when entering the endgame.
Some pawn structures are better in the end game than others, so you will consider this throughout the middle game in trying to maintain your strength when it comes to the nitty-gritty battle for ultimate supremacy.
Pawns may be the least valuable piece on the board when it comes to basic chess piece values at the beginning of the game, but it is widely accepted that in the end game, pawns become more and more important, if they are well set up and can play a part in the attack and threat of promotion. Your opponent will have to consider them too, and not allow you to stroll a passed pawn to the other side, this restricts your opponent from focussing 100% on attacking your King.
Pawn Structure Fundamentals
The importance of pawn structure can not be understated, the strongest pawn structure being one that contains ‘connected pawns’; that is, pawns that protect each other in whatever structure they appear.
Pawn structure can seem a complicated and in-depth subject to begin with, but spend some time learning the fundamentals, and you will soon learn to recognise and aim for structure in your plans to dictate and facilitate your overall chess strategy.
Pawn Chains
A pawn chain is a group of pawns on a diagonal that protect each other in turn. A pawn chain can prevent the progression of your opponent down one side of the board making it hard for them to formulate an attack, and a chain can also be a formidable attacking strength in the endgame if it remains intact.
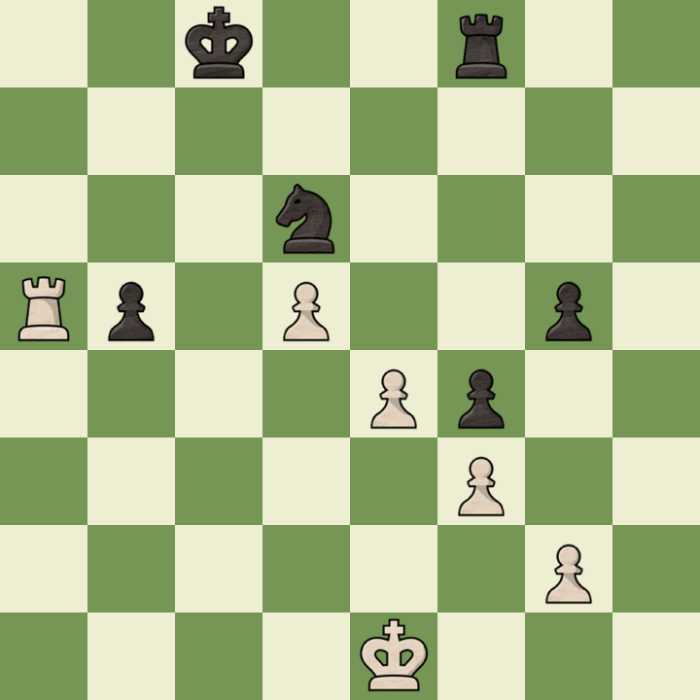
In this example of a pawn chain above, despite the fact that Black has an extra Knight and only one fewer pawns, the strength of the chain determines that white is way ahead in this game and should find it hard to lose with the pawns supporting each other
Pawn Islands
A pawn island in chess is a weakness in pawn structure represented by groups of pawns on adjacent squares but disconnected from other pawns with open files between them. The fewer the pawns in the island, the weaker they become, a single pawn would be considered isolated
- PRO: Will allow players to correctly determine the pawn structure’s health.
- CON: Can sometimes be unreliable.
Isolated Pawns
An isolated pawn in chess occupies a square with no friendly pawns on adjacent squares, leading to a weakness in pawn structure if unprotected. By protecting an isolated pawn with a more valuable and versatile piece, a player may be weakening their entire strategic position in the game.
- PRO: Are usually the ones that become a passed pawn.
- CON: Can no longer be defended by other pawns.
Hanging Pawns
Hanging pawns are a pair of same-colored pawns on horizontally adjacent squares where neither protects the other and the files on either side of the pair have no friendly pawn presence. Wilhelm Steinitz , the first chess world champion, coined the phrase originally.
- PRO: The two pawns can potentially support each other’s advance but need space to move
- CON: One of the two pawns will eventually become a backward pawn.
Backward Pawns
Backward pawns are pawns that sit behind pawns on adjacent squares that can not be advanced without risking being captured. Because of their frail positioning backward pawns are generally considered to be a positional disadvantage in pawn structure.
- PRO: Can be used to push through a locked pawn setup.
- CON: Can easily be targeted for attacks.
Doubled Pawns
Doubled pawns in chess occur when two pawns of the same color appear on the sale file due to the capture of an enemy piece and the more advanced pawn can obstruct the movement of the one in the rear. Doubled pawns can cause positional disadvantage to a player but are sometimes unavoidable.
- PRO: Can occasionally control key areas on a critical rank.
- CON: The upper pawn blocks the lower pawn’s advance.
Passed Pawns
A passed pawn in chess is a pawn that has no opposing pawns on either the same rank or the ranks adjacent on either side meaning that it can advance to the opposing back rank for promotion purposes without opposing pawn intervention.
- PRO: Provides attacking options that the opponent has to consider at all times
- CON: Can be picked off if not defended well
Pawn Majority
A pawn majority occurs when one player has more pawns on one side of the board than the other player. This means that if both players advance their pawns in the endgame the one with the pawn majority will come out on top. You can cut the board into two to create an imaginary line, this will be composed of the right and left side. This can be the basis to determine the pawn majority.
- PRO: The player with the pawn majority will win in a pawn slugfest.
- CON: A pawn majority has to be well-positioned so as not to block the development of major pieces.